THE UBER EATS BUSINESS MODEL
UberEats business model has given inspiration to the budding entrepreneurs and has led to a large number of on demand startups in the food delivery vertical. And hence, many traditional value chains in the food industry stand disrupted.
The company made its foray into food delivery in August, 2014 with the launch of the Uber Fresh service in Santa Monica, California. In 2015, the platform was renamed to Uber Eats and is now available in 71 cities across 24 countries. According to a report, Uber Eats’ monthly unique user numbers are indeed growing at a rapid rate: in August 2017, its 5.3 million monthly unique users represented a 530% increase since last September.
Uber Eats plays dual roles- it’s an aggregator as well as a delivery agent. On one hand, it builds on the traditional model for food delivery, offering access to multiple restaurants through a single online ordering app. On the other, it has it’s own logistics network too, providing delivery for restaurants that don’t have their own drivers. UberEats’ was released as a standalone application from the customer application for booking Uber rides. Tailored restaurant recommendations, advanced search filters, customizable delivery details, and the ability to track your order in the app are some features they’ve introduced.
THE UBER EATS ECOSYSTEM
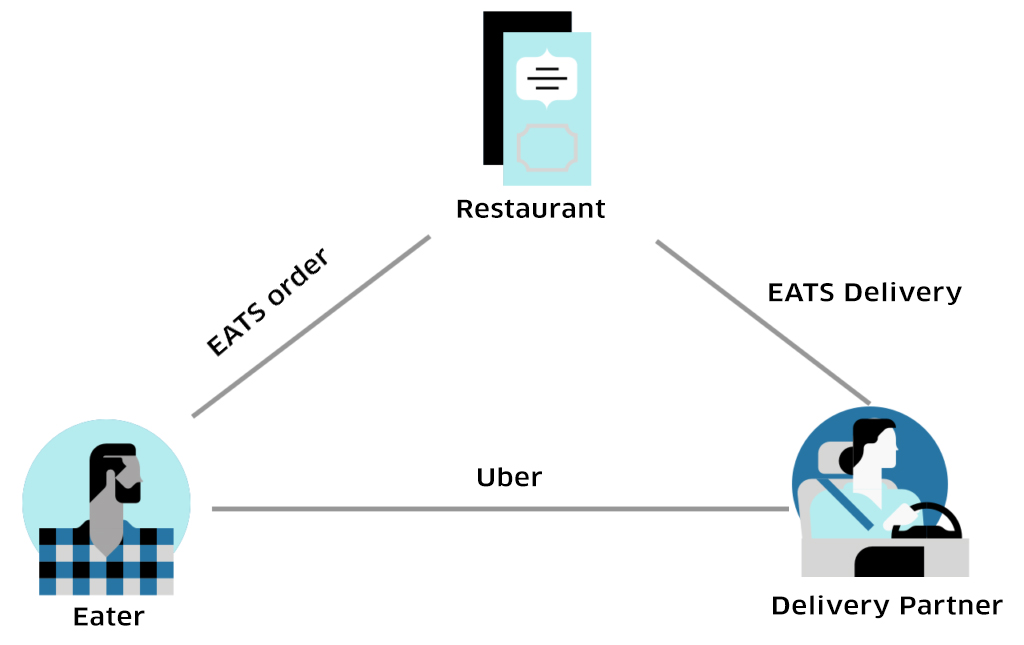
The UberEats Ecosystem
UberEats has the following 4 components-
- Customer- Real-time Order Placing
Flexible Menu, Timelines and Locations.
The customer chooses from the extensive list of offerings in terms of restaurants and menus. In such cases, UberEats works like any other food delivery company. The only advantage being the huge fleet of Uber cars available in different areas. - Customer- Custom Order Placing
Specific Product, Fixed delivery time, Particular Location.
This works like custom ordering with everything decided by the Customer. Deliveries are made according to the Customer’s chosen time. Sometimes, Uber also pre-picks items in bulk for all similar orders which makes the process faster and more efficient - Courier Partners (Uber Drivers)
These are the Uber Drivers that have registered or signed up to be a part of the delivery network. They’re allocated orders on the basis of the location they’re at and also, the proximity to both, the customer as well as the restaurant from which the order needs to be picked up. - Restaurant Partners
The shift in customer behaviour towards on-demand food delivery apps is driving conventional businesses to have a virtual presence on an app like UberEats.
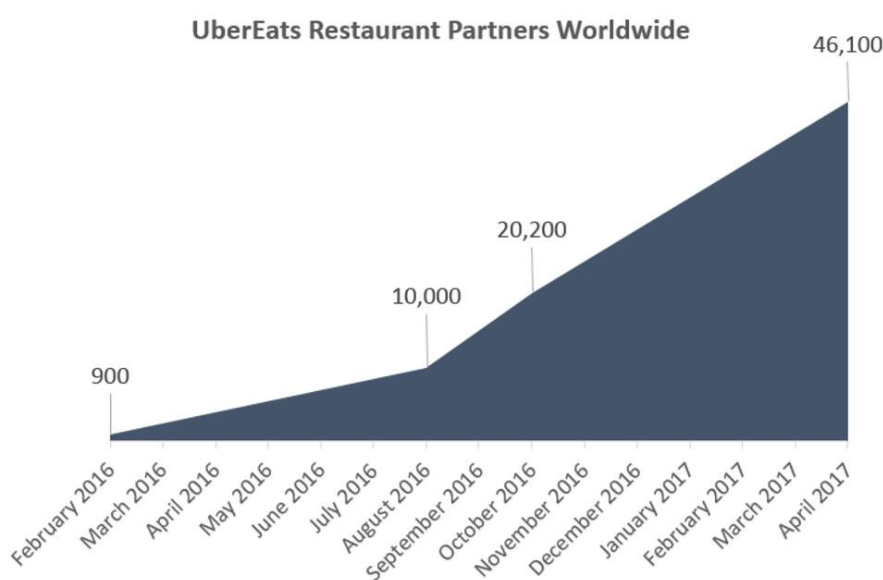
UberEats Restaurant Partners
HOW DOES UBEREATS MAKE MONEY?
- Delivery Fee from Customers
The pricing model for UberEats is a base price plus surcharges. Lunch and Dinner hours are the peak hours and in those hours, sometimes the menu and the restaurants become limited. - Revenue Sharing from Restaurants
UberEats earns itself some recurring revenue sharing for the orders fulfilled by UberEats. This ranges from 15% to 40%, depending on the maturity of the market. - Advertising income from Restaurant partners
They charge their restaurant partners a marketing fee to come up as top searches whenever a customer looks at the listed restaurants. And with the rapidly increasing number of restaurants, it becomes even more important for restaurants to gain some visibility on the app.
THE COST TO MAKE AN APP LIKE UBER EATS
Having a market share in the food delivery industry is extremely important and this “billion-dollar war” will only get tougher as saturation increases. Only time will tell which companies will make it to the top.
The cost to make an app like UberEats is based on a number of factors. Building an MVP for an On-Demand Platform involves creating web/mobile interfaces for both supplies via the driver’s app & restaurant’s app and demand through the user’s app. Another important component is the nerve centre/admin panel that doubles up as a CRM and a Dashboard to moderate and controls your critical operations i.e. the UberEats Dashboard. The app for the Restaurant owners would enable them to manage their menus, pricing, inventory availability and to provide offers and discounts to their customers. Everything is glued together by the APIs that operate on top of central databases and control logic – part of the backend framework that runs on the cloud.
Subscribe to stay ahead with the latest updates and entrepreneurial insights!

Subscribe to our newsletter
Get access to the latest industry & product insights.