- Products
- Solutions
- Learn
- Partner
- Try Now
What is Postmates?
Postmates is an on-demand goods delivery platform having a presence in more than 100 metropolitan areas in the USA that enables people to get anything from local stores delivered at their doorstep for a small fee. The business model of Postmates is often said to be similar to Uber, but instead of taxis, Postmates enables a customer to get goods from local stores. Postmates delivers goods with the help of their human courier networks which enables people to order anything from anywhere within the city. Just like Uber drivers, Postmates couriers get order notification on their mobile device and GPS is used by the company to match demand and supply in the shortest possible time.
Postmates unique business model has fetched a good amount of funding from investors and has helped the company acquire a large customer base. Postmates was launched in the year 2011 and in a short period of 4 years, it has come out as a huge success. Postmates has got official tie-ups with Apple, Mcdonalds, Starbucks, Walgreens, Chipotle and many other well-known companies.
Founders, Funding Received and Facts
Founders: Sam Street, Sean Plaice and Bastian Lehmann.
Company Headquarters: San Francisco, California.
Funding received by Postmates: $138M (As of November 2015)
Company Valuation: $500 M
Number of daily orders processed: 7500 (As of 2015 start)
Average order size: $40
Postmates Funding Timeline:
Salient Features of Postmates
- Enables people to order anything from anywhere within the city.
- Postmates charges a nominal delivery fee which depends on the distance covered from pick up point and drop off point.
- Special featured stores.
- The delivery guys or couriers who work with Postmates are also called Postmates.
- Deliveries are made within 1 hour.
- Postmates is available 24 hours a day and 365 days a year.
- The minimum delivery fee is $5 but often there are offers in particular areas with even lower delivery fee.
- Customer can track the location of the delivery guy after placing the order.
Postmates 3 customer segments explained
Postmates serves 3 different types of segments as explained below:
Customers: Customers for postmates are the ones who are willing to spend a little more than the exact price of an article in order to get it delivered at their doorstep. People
Merchants: Postmates ties-up with local merchants and provides them with a platform with an opportunity to reach out to people who want goods delivered at their location. These merchants are happy to pay a percentage of the total billed amount to Postmates for their delivery service. Hiring own staff to make deliveries is obviously a costlier option as compared to paying a small percentage of the bill to Postmates.
Delivery Persons: Delivery personals for postmates are the people who want to earn money by working according to their own schedule. These human couriers are called postmates. According to the business model, postmates driver get 80% of the delivery fee and rest 20% is kept by the company. According to Postmates, a delivery guy can earn upto $25 per hour.
Value Propositions
Postmates business model offers excellent value propositions for customers, delivery personal as well as local stores. Let’s understand the value provided by Postmates to these customer segments.
Users:
- Users can order anything from local partner stores.
- Postmates is available 24 hours a day and all 365 days a year.
- Get things delivered in as less as 1 hour.
Merchants:
- They get an extended customer base.
- They can serve their own customers at their doorstep through Postmates.
- Postmates provides online visibility to the merchant through their platform.
Delivery Persons:
- They can work according to their own schedule.
- According to postmates revenue model, delivery guys get 80% of the delivery fee.
- The more they deliveries they make, the more they earn.
Postmates Business Model Canvas
We here at Juggernaut made a Business model canvas for postmates on the lines of the business model generation canvas proposed by Alexander Osterwalder. You may go through the following canvas:
The 4 step model about how Postmates works
- Step 1 (Browse stores and products):
The first step in the business model of Postmates is about creating a demand. People have a smartphone app as well as a desktop application which lets them request an article at their doorstep.
- Step 2 (Payment):
An order is said to be received at Postmates only once it is paid. The delivery fee is added to the actual price of the order depending on the pickup and drop-off location. All payments are handled by Postmates.
- Step 3 (Matching):
As soon as an order is confirmed after payment, a notification about the order is sent to a Postmate (delivery guy) who is stationed nearest to the store. He shops for your order and delivers it at your doorstep within one hour. Postmates travel by bike or by car. The matching process is such that all orders are processed within 1-hour time frame.
- Step 4 (Tracking, Receiving Order & Tips):
Another excellent feature in the Postmates business model is that a user is able to track the exact location of the postmate who is on the way to deliver their order. Postmate has an option to send a text to the user in case of delays. Tipping a postmate is entirely upto the user. The company says that no tips should be given but a postmate earns some tip in majority of orders.
How Postmates earns revenue
If you are looking forward to start your own ‘on demand delivery’ business, one important thing you might be interested in is the revenue model. Postmate’s business and revenue model have been the backbone for the company which has led to its massive success. Let’s see how postmates earns money.
There are 3 main revenue streams for Postmates:
1. Delivery Fee
Postmates charges users a small delivery fee for each order processed. This delivery fee normally starts from $5 but often there are specific ongoing offers where the company offers $3 or even lower delivery. However, 80% of the total delivery fee goes to the delivery guy and rest 20% is Postmates revenue.
2. Convenience Fee
Apart from the delivery fee (majority of which goes to the delivery guy), Postmates has a flat fee of 9% as convenience fee over each order. According to Techcrunch, there is no cap on this fee of 9%. People are happy to pay this convenience fee as it is more convenient to get goods at their doorstep without spending time and fuel. This adds up to Postmates revenue.
3. Merchant Programme
Postmates recently launched a merchant program where it ties up with local stores and signs an official agreement. The main purpose of this agreement is that the store pays a certain percentage of the total bill to postmates for their service adding up to company’s revenue.
Postmates Growth: How they find customers
You might be clear with Postmates business and revenue model but the main challenge for any startup in the delivery sector is to gain users and reach some transactions. This brings us to a question ‘How does Postmates find customers?’ Well, Postmates has become widely known on-demand delivery startup by now and it has reached a stage where users come automatically (through word of mouth). In earlier days, Postmates has made use of digital marketing, offline advertisements and other marketing methods.
Here’s a growth graph of Postmates. (As published on TechCrunch).
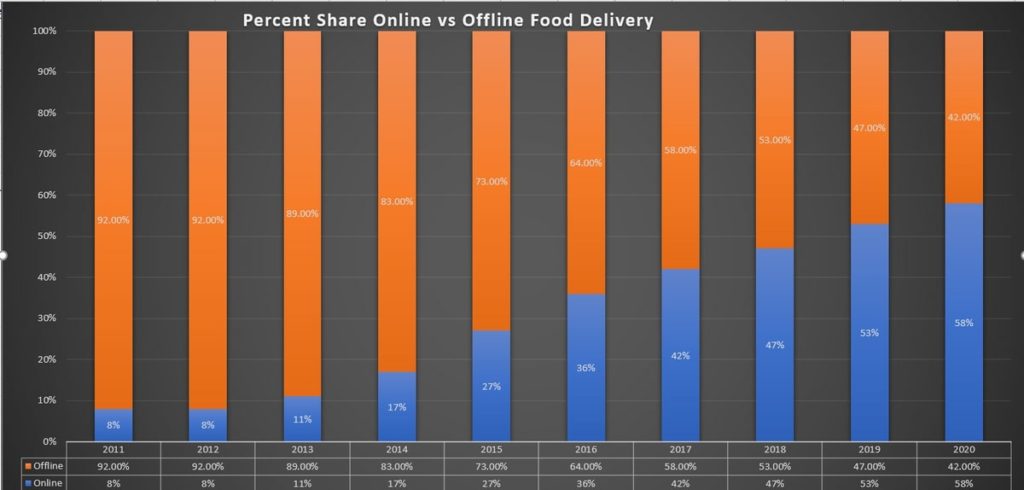
In recent developments, Postmates has taken the leap to go Public. Catch the insights here.
Subscribe to stay ahead with the latest updates and entrepreneurial insights!

Subscribe to our newsletter
Get access to the latest industry & product insights.